To track the hot spots of mitochondria and solve the difficult problems in respiratory chain research
In addition to being a key organelle for intracellular energy generation, mitochondria are also involved in metabolic processes such as apoptosis, free radical production, and lipid metabolism. Some studies have reported that mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to the pathology of many common diseases, including neurodegeneration, metabolic diseases, heart failure, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and protozoan infections. Therefore, mitochondria represent an important drug target for these highly prevalent diseases. Several strategies aimed at therapeutic restoration of mitochondrial function are emerging, and a few agents have entered clinical trials.
The role of the respiratory chain represents the most basic function of mitochondria. The hydrogen carrier and electron carrier in the respiratory chain are carriers that can transfer hydrogen atoms or electrons. Since hydrogen atoms can be seen as composed of protons and extranuclear electrons, the hydrogen carrier is also an electron carrier. The essence of the hydrogen and electron transporters are enzymes, coenzymes, prosthetic groups or cofactors. Meanwhile, oxidative phosphorylation is a process in the respiratory chain that promotes the conversion of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to triphosphate (ATP) through a proton gradient generated by REDOX reactions. This process mainly occurs in the last step of cellular respiration, the electron transport chain of the respiratory chain on the inner mitochondrial membrane.
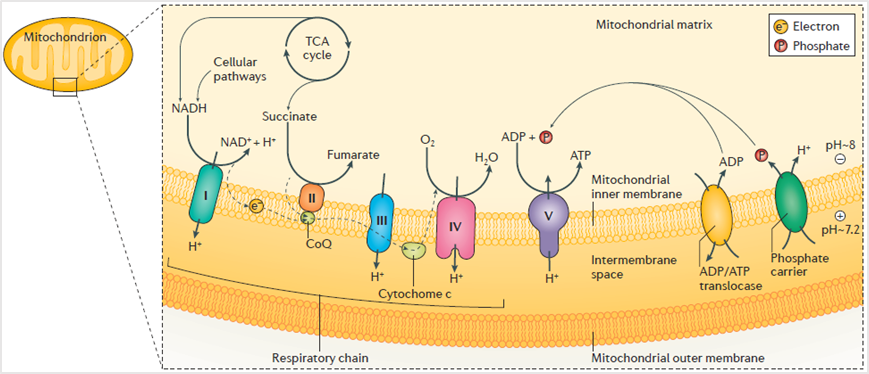
Image from the Web, Schematic diagram of oxidative phosphorylation
Mitochondrial respiratory chain complex activity is inseparable from mitochondrial function. Defects in mitochondrial respiratory chain enzymes can cause mitochondrial diseases. Long-term inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex activity may lead to neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease, Down's syndrome, Leigh's syndrome, etc.
Therefore, mitochondrial respiratory chain complex activity is often used as an indicator of mitochondrial toxicity-induced neurological defects.
What are the components of the mitochondrial respiratory chain complex?
Complex I
- The largest component of the respiratory chain, with a mass of about 1 mda, consists of 14 core subunits plus 31 additional subunits;
- Seven inner membrane embedded core subunits (ND1-ND6, ND4L) are encoded by the mitochondrial genome and are the innermost part of Complex I, including all catalytic sites; Matrix arm: NADH oxidation site, including core subunits (NDUFS1, NDUFV1, NDUFS2, NDUFV2, NDUS3, FNDUFS7, NDUFS8), eight Fe-S clusters, and electron acceptor flavin single nucleotide;
- Assembly requires 20 auxiliary assembly factors;
- Assembly module (intermediate) : 6。
Complex II
1.Tricarboxylic acid cycle +OXPHOS, an important player in cell metabolism;
2. four subunits (SDHA, SDHB, SDHC, SDHD) encoded by the nuclear genome, soluble subunits SDHA and SDHB containing FAD and three Fe-S clusters responsible for succinate reduction and electron transfer to coQ; Soluble subunits SDHA and SDHB are connected to the mitochondrial inner membrane through membrane-embedded subunits SDHC and SDHD.
3.SDHAF1-SDHAF1 is required for subunit assembly. In the assembly process, the cofactors are first loaded on SDHA and SDHB, while SDHC and SDHD form dimers on the Mito inner membrane, and then the soluble subunits combine with the dimers to form the complete complex II;
4. At present, the exact path of proton transfer of electron through complex II leading to coenzyme Q reduction is still unknown.
Complex III
1.Cytochrome c reductase: a dimer structure, each monomer contains three subunits (CYb, CYC1, Rieske iron-sulfur protein);
2.In addition to the catalytic subunit, additional subunits are also included, the composition of which varies from species to species. Mammals contain eight such subunits (core 1 protein UQCRC1, core 2 protein UQCRC2, UQCRH, UQCRB, UQCRQ, UQCR10, UQCR11).
3.Complex III is required for the correct assembly of Complex I and Complex IV, suggesting functional crosstalk between ETC complexes.
Complex IV
1.Cytochrome c reductase: a dimer structure, each monomer contains three subunits (CYb, CYC1, Rieske iron-sulfur protein);
2.In addition to the catalytic subunit, additional subunits are also included, the composition of which varies from species to species. Mammals contain eight such subunits (core 1 protein UQCRC1, core 2 protein UQCRC2, UQCRH, UQCRB, UQCRQ, UQCR10, UQCR11).
3. Complex III is required for the correct assembly of Complex I and Complex IV, suggesting functional crosstalk between ETC complexes.
What are the advantages of this series?
- The operation process is simple and quick: compared with the spectrophotometer method, the micromethod makes the experimental operation simpler and faster, saves time, and is suitable for the detection of multiple samples;
- The detection results are more sensitive and accurate: the experimental principle is carefully designed, and the standard substance and standard curve are provided, and each product provides the best method for determining the protein concentration of the sample according to the actual situation;
- Compatible with various types of experiments: animal tissue samples, plant tissue samples, cell samples;
- Provide authentic and reliable sample verification results and references.
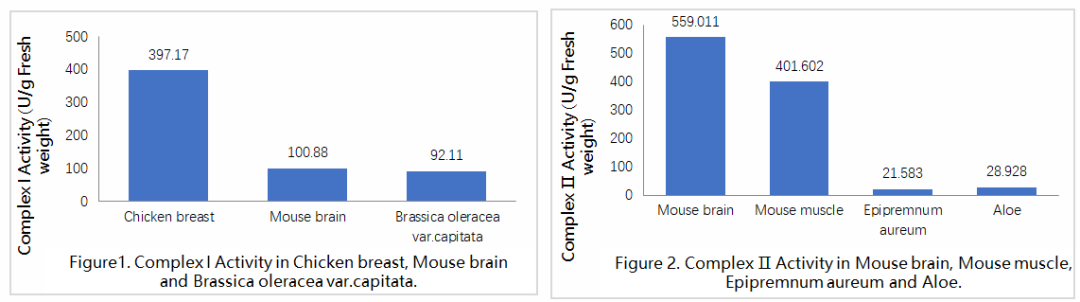
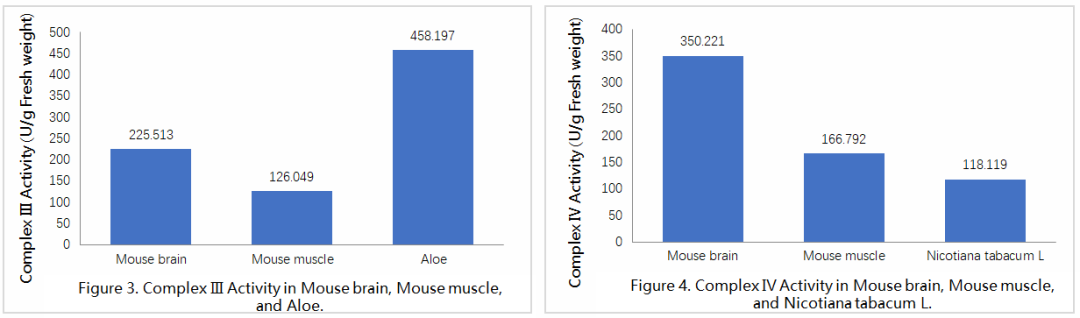
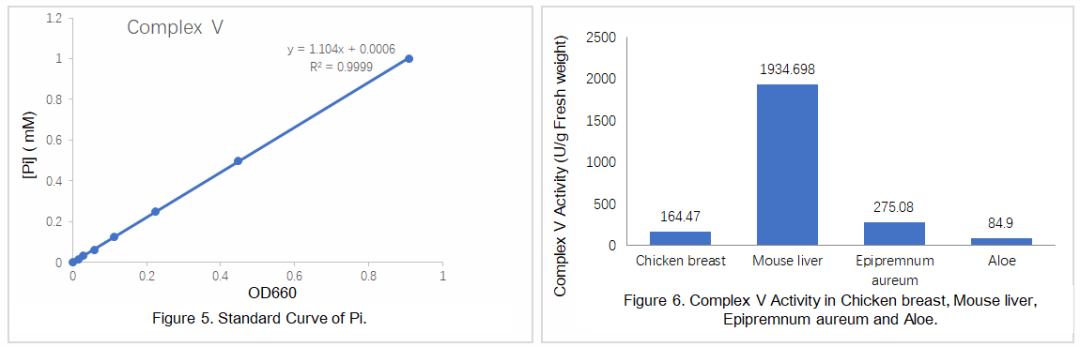
References
- Yu T, Zhang Y, Zheng W Q, et al.Selective degradation of tRNASer(AGY) is the primary driver for mitochondrial seryl-tRNA synthetase-related disease. Nucleic Acids Research. IF: 19.16.
- S Huo, Q Wang, W Shi, L Peng. ATF3/SPI1/SLC31A1 signaling promotes cuproptosis induced by advanced glycosylation end products in diabetic myocardial injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. IF: 6.208.
- Liu, Yingxin, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in metabolic disorders induced by per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance mixtures in zebrafish larvae. Environment International. IF: 11.8.
- Liu, Yuqiang, et al.An Fgr kinase inhibitor attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation via the SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway. Journal of Translational Medicine. IF:7.4.
product recommendation
| Product No. | Product Name | Sizes |
| KTB1850 | CheKine™ Micro Mitochondrial complex I Activity Assay Kit | 48 T/96 T |
| KTB1860 | CheKine™ Micro Mitochondrial complexⅡ Activity Assay Kit | 48 T/96 T |
| KTB1870 | CheKine™ Micro Mitochondrial complex Ⅲ Activity Assay Kit | 48 T/96 T |
| KTB1880 | CheKine™ Micro Mitochondrial complex Ⅳ Activity Assay Kit | 48 T/96 T |
| KTB1890 | CheKine™ Micro Mitochondrial complex Ⅴ Activity Assay Kit | 48 T/96 T |











