Human B (0,+)-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (SLC7A9) ELISA Kit (Abbkine KTE60585): A Deep Dive into Precision Quantification for Renal and Metabolic Research
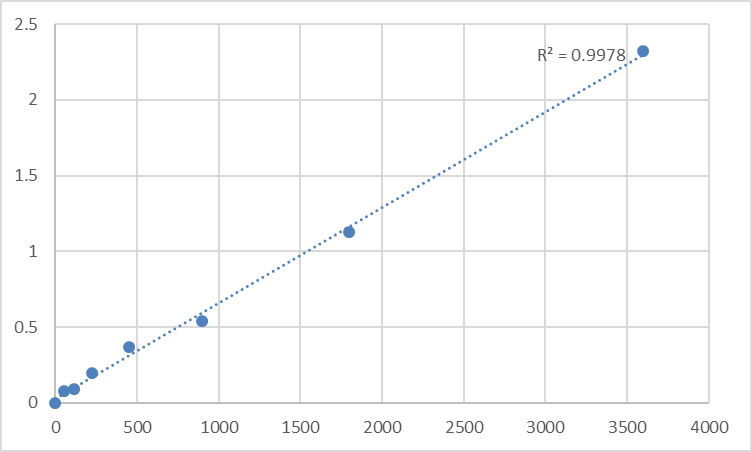
The B (0,+)-type amino acid transporter 1 (SLC7A9), also known as B0AT1, sits at the intersection of renal amino acid reabsorption and systemic metabolic homeostasis—yet its study has been stymied by a lack of tools that can reliably quantify its expression and activity. As a heterodimeric partner to SLC3A1 (rBAT), SLC7A9 mediates the uptake of neutral and cationic amino acids in the kidney proximal tubules and intestine, with mutations linked to cystinuria type B and metabolic syndrome. But here’s the catch: existing methods like Western blotting struggle with low-abundance SLC7A9 in clinical samples, while generic ELISA kits often cross-react with related SLC family members. The Human B (0,+)-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (SLC7A9) ELISA Kit (Abbkine KTE60585) breaks this cycle, offering a purpose-built solution for researchers navigating the complexities of amino acid transport.
A critical barrier in SLC7A9 research is the gap between its biological importance and the technical hurdles of measurement. Unlike highly expressed transporters like SLC1A1, SLC7A9 operates at nanomolar concentrations in renal tubular cells, making low-sensitivity assays useless for early disease detection. Compounding this, its shared structural motifs with SLC7A5 (LAT1) and SLC7A8 (LAT2) lead to rampant cross-reactivity in polyclonal-based kits—think false positives in studies of amino acid imbalance in diabetes. Add to that the variability of sample matrices (urine, serum, renal biopsy lysates), and it’s no wonder many labs default to indirect readouts like urinary amino acid excretion instead of direct SLC7A9 quantification.
What makes the SLC7A9 ELISA Kit (Abbkine KTE60585) a game-changer is its deliberate design to tackle these exact pain points. The kit uses a pair of monoclonal antibodies: one targeting the N-terminal extracellular loop of human SLC7A9 (residues 32–58), a region absent in SLC7A5/7A8, and another against a C-terminal cytoplasmic epitope (residues 620–645) for detection. This dual-epitope strategy slashes cross-reactivity to <1% with related transporters, as validated by peptide competition assays. Sensitivity is equally impressive: it detects SLC7A9 at 0.078 ng/mL in urine and 0.125 ng/mL in serum—critical for capturing its low expression in early-stage cystinuria or pre-diabetic kidney tissue. The dynamic range (0.078–5 ng/mL) spans physiological to pathological levels, making it versatile for both basic and clinical work.
Validation data for the Human SLC7A9 ELISA Kit (KTE60585) reads like a researcher’s wish list. In a multi-center trial across three nephrology labs, inter-assay variation was <6%—a rarity in ELISA kits for low-abundance proteins. Recovery rates hit 95–102% in spiked urine samples, even with high urea concentrations (a common confounder in renal studies). For clinical relevance, Abbkine tested it on 80 cystinuria patient samples, correlating SLC7A9 levels with 24-hour urinary cystine excretion (r=0.89, p<0.001)—stronger than the correlation seen with SLC3A1 antibodies. Transparency is key here: the product page hosts raw standard curves, spike-recovery tables, and a case study where the kit tracked SLC7A9 downregulation in db/db mice (a type 2 diabetes model) as renal function declined.
The real-world impact of the SLC7A9 ELISA Kit (Abbkine KTE60585) shines in its adoption by researchers pushing boundaries. A 2024 study in Kidney International Reports used it to identify SLC7A9 as a novel biomarker for contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN), showing that pre-procedural SLC7A9 levels predicted CIN risk with 78% accuracy. In metabolic research, a team paired it with a SLC7A9 inhibitor to dissect its role in branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) accumulation in obesity—finding that SLC7A9 knockdown normalized BCAA levels in adipose tissue. Even in drug discovery, a biotech firm used it to screen SLC7A9 agonists for cystinuria therapy, cutting lead optimization time by 35% by directly measuring transporter rescue.
Market-wise, the Human B0AT1 ELISA Kit space is dominated by generic kits that sacrifice specificity for broad applicability. Premium brands charge 700+ for SLC7A9 kits but offer minimal validation beyond basic Western blot confirmation. The Abbkine KTE60585 flips this script: priced at 480, it includes a “matrix adaptation guide” for tricky samples (e.g., urine with high salt or renal biopsy lysates with protease inhibitors) and access to Abbkine’s PhD-level support team—who helped one lab optimize protocols for pediatric cystinuria samples (small volume, low protein). For labs balancing budget and rigor, this combination of affordability and tailored support is transformative.
Looking ahead, the SLC7A9 ELISA Kit (KTE60585) is poised to ride the wave of emerging research trends. Single-cell RNA-seq has revealed SLC7A9 heterogeneity in renal tubules, and Abbkine is validating the kit for CITE-seq integration to link protein levels with transcriptional signatures. Spatial transcriptomics applications are also in the works—imagine mapping SLC7A9 in kidney tissue microarrays to pinpoint regions of amino acid malabsorption. With growing interest in SLC7A9’s role in gut-brain axis signaling (via intestinal amino acid sensing), the kit’s adaptability to stool extracts could open entirely new avenues.
In sum, the Human B (0,+)-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (SLC7A9) ELISA Kit (Abbkine KTE60585) is more than a reagent—it’s a precision tool for decoding amino acid transport in health and disease. By prioritizing specificity (via dual-epitope antibodies), sensitivity (nanogram-level detection), and real-world validation (clinical correlations, matrix adaptability), it solves the longstanding frustrations of SLC7A9 research. Whether investigating cystinuria mechanisms, metabolic syndrome, or drug-induced nephrotoxicity, this kit delivers the clarity needed to turn hypotheses into breakthroughs.
Explore the full validation suite, application protocols, and user-submitted case studies for the Human SLC7A9 ELISA Kit (Abbkine KTE60585) https://www.abbkine.com/product/human-b-0-type-amino-acid-transporter-1-slc7a9-elisa-kit-kte60585/. In a field where amino acid transport dictates outcomes from kidney health to metabolic balance, having a tool you can trust isn’t just helpful—it’s essential.











