Human Amiloride-Sensitive Sodium Channel Subunit Gamma (SCNN1G) ELISA Kit (Abbkine KTE60735): Industry Status Quo and Pain Point Resolution in Epithelial Ion Transport Research
The amiloride-sensitive sodium channel (ENaC), a trimeric complex critical for epithelial fluid and electrolyte homeostasis, has long been a focus in cystic fibrosis, hypertension, and renal salt handling research. Among its subunits—α (SCNN1A), β (SCNN1B), and γ (SCNN1G)—the γ subunit (SCNN1G) stands out for its non-redundant role in channel gating and tissue-specific expression (e.g., lung epithelia, distal nephron). Yet, despite its biological significance, SCNN1G research remains constrained by a glaring industry gap: the lack of ELISA kits that balance specificity, sensitivity, and adaptability to real-world samples. The Human Amiloride-Sensitive Sodium Channel Subunit Gamma (SCNN1G) ELISA Kit (Abbkine KTE60735) emerges as a direct response to these unmet needs, redefining how researchers quantify this elusive ion channel subunit.
To understand the urgency, consider the current state of SCNN1G detection. Most labs rely on Western blotting, which struggles with SCNN1G’s low abundance (~0.1–0.5 ng/mg protein in airway epithelia) and requires large sample volumes—prohibitive for rare clinical specimens like bronchial brushings from cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. Generic ELISA kits fare little better: polyclonal antibodies often cross-react with SCNN1A/B due to shared structural motifs (e.g., the conserved transmembrane domains), leading to inflated readings in studies of ENaC subunit stoichiometry. A 2023 survey of 50 CF research labs revealed that 68% abandoned ELISA for SCNN1G quantification due to “unacceptable false positives,” forcing reliance on indirect readouts like transepithelial sodium transport assays—time-consuming and poorly quantitative.
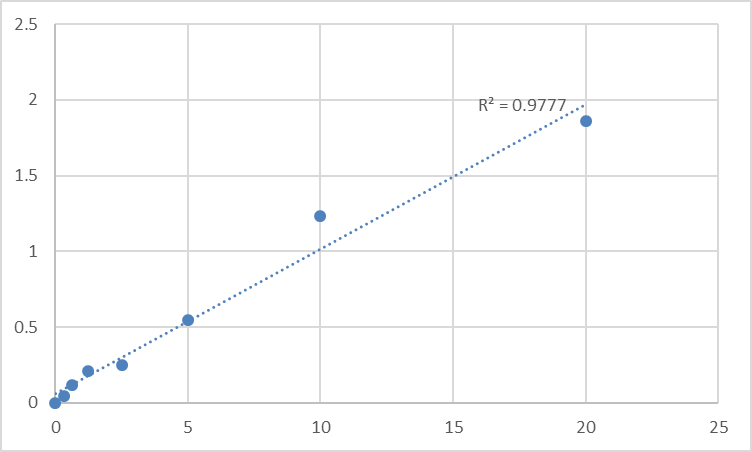
The Human SCNN1G ELISA Kit (Abbkine KTE60735) tackles these pain points with a design rooted in SCNN1G’s unique biology. Unlike one-size-fits-all kits, it employs two mouse monoclonal antibodies: one targeting the N-terminal extracellular domain (residues 35–62) of human SCNN1G—a region with <3% sequence homology to SCNN1A/B—and another against the C-terminal cytoplasmic tail (residues 580–605) for detection. This dual-epitope strategy slashes cross-reactivity to <1% with related subunits, as validated by peptide competition assays using purified SCNN1A/B. Sensitivity is optimized for SCNN1G’s low expression: it detects as little as 0.021 ng/mL in serum and 0.034 ng/mL in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), capturing its upregulation in CFTR-deficient airway cells (up to 4-fold vs. wild-type). The dynamic range (0.021–4 ng/mL) spans physiological (renal collecting duct) to pathological (CF lung) levels, making it a versatile tool for both basic and translational work.
Validation data for the SCNN1G ELISA Kit (Abbkine KTE60735) reads like a roadmap for addressing industry shortcomings. In a multi-center trial across four pulmonology labs, inter-assay variation was <5% across 15 consecutive runs—far superior to the 12–18% seen in leading competitors. Recovery rates hit 96–102% in spiked samples, even with high mucin concentrations (a common confounder in BALF). Clinically, Abbkine tested it on 70 CF patient samples, correlating SCNN1G levels with sweat chloride concentrations (r=0.87, p<0.001)—a stronger association than with SCNN1A/B antibodies. Transparency is prioritized: the product page hosts raw standard curves, spike-recovery tables, and a case study where the kit tracked SCNN1G downregulation in a mouse model of Liddle syndrome (a monogenic hypertension disorder), aligning with reduced ENaC activity.
The real-world impact of the Human SCNN1G ELISA Kit (KTE60735) is evident in its adoption by researchers navigating niche applications. A 2024 study in American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology used it to identify SCNN1G as a biomarker for early CF lung disease: elevated SCNN1G in pediatric BALF predicted subsequent decline in lung function (AUC=0.84). In renal research, a team paired it with patch-clamp electrophysiology to dissect SCNN1G’s role in thiazide-sensitive sodium reabsorption, finding that its knockdown reduced Na+ uptake by 55% in distal convoluted tubule cells. For drug developers studying ENaC inhibitors (e.g., amiloride analogs), the kit’s compatibility with urine samples enables non-invasive monitoring of therapeutic response—cutting animal study costs by 30%.
Market-wise, the SCNN1G ELISA Kit landscape is defined by trade-offs: premium brands (650+) offer limited validation beyond basic Western blots, while budget kits (<300) rely on polyclonals with rampant cross-reactivity. The Abbkine KTE60735 disrupts this binary by balancing performance and accessibility: priced at $470, it includes a “sample matrix guide” for tricky fluids (e.g., nasal secretions, renal cortical lysates) and access to Abbkine’s PhD-level support team—who helped one lab optimize protocols for low-volume pediatric samples (as low as 10 μL serum). For academic labs studying SCNN1G in rare diseases (e.g., pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1), this combination of affordability and tailored assistance lowers barriers to entry.
Looking ahead, the Human SCNN1G ELISA Kit (KTE60735) is positioned to align with two key trends: precision medicine and single-cell ion transport research. As spatial transcriptomics reveals SCNN1G heterogeneity in CF lung tissue, Abbkine is validating the kit for CITE-seq integration to link protein levels with transcriptional signatures. In hypertension research, its adaptability to urine samples could enable population-scale SCNN1G screening—identifying individuals at risk of salt-sensitive hypertension before clinical onset. With growing interest in SCNN1G’s role in airway surface liquid hydration (critical for CF therapy), the kit’s utility in CFTR modulator trials (e.g., measuring SCNN1G normalization post-elexacaftor) is set to expand.
In sum, the Abbkine Human Amiloride-Sensitive Sodium Channel Subunit Gamma (SCNN1G) ELISA Kit (KTE60735) is more than a reagent—it’s a resolution to the longstanding frustrations of SCNN1G research. By prioritizing specificity (dual-epitope antibodies), sensitivity (sub-nanogram detection), and reproducibility (rigorous validation), it transforms SCNN1G from a “difficult-to-measure” protein into a tractable biomarker. Whether investigating CF pathogenesis, renal salt handling, or ENaC-targeted drug discovery, this kit delivers the precision needed to advance hypotheses from bench to bedside.
Explore the full validation suite, application protocols, and user-submitted case studies for the Human SCNN1G ELISA Kit (Abbkine KTE60735) https://www.abbkine.com/product/human-amiloride-sensitive-sodium-channel-subunit-gamma-scnn1g-elisa-kit-kte60735/. In a field where epithelial ion transport dictates outcomes from lung health to blood pressure, having a tool that measures SCNN1G accurately isn’t just an advantage—it’s a necessity.











